RECENT POSTS
Share:
- September 4, 2024
Choosing the right combustible and toxic gas detectors is paramount to ensuring safety in industrial settings where hazardous gases are present. Here is a guide to help you choose the right detector based on the properties of the gas and the environment:
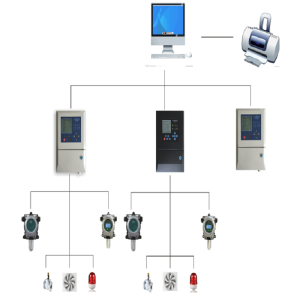
Selection Criteria for Gas Detectors
- For Hydrocarbon Combustible Gases:
Catalytic Combustion Detectors: These are commonly used for hydrocarbons and provide a reliable and cost-effective solution. They work by igniting the gas on a catalytic bead, which increases the temperature and changes the resistance, indicating the presence of gas.
Infrared (IR) Gas Detectors: IR detectors are more suitable in environments where gases like sulfur, phosphorus, silicon, lead, halogens, or other elements that can poison the detection element are present. They are less prone to interference and can operate in a wider range of conditions.
- In Oxygen-Deficient or Highly Corrosive Environments:
Infrared (IR) Gas Detectors: IR detectors are unaffected by the lack of oxygen and are more resistant to corrosive atmospheres compared to catalytic detectors. They are ideal for environments where the oxygen content is low or where there is a risk of corrosion.
- Hydrogen Detection:
Catalytic Combustion Detectors: These are effective for hydrogen detection due to their sensitivity to a wide range of combustible gases.
Electrochemical Detectors: These can detect hydrogen specifically and are useful in environments where other gases might interfere.
Thermal Conductivity Detectors: These detectors are sensitive to changes in thermal conductivity and can be used for hydrogen detection.
Semiconductor Detectors: Semiconductor sensors can detect hydrogen and are often used in portable devices.
- Single Component Combustible Gas Detection:
Thermal Conductivity Detectors: These are particularly useful for detecting gases with a high thermal conductivity difference compared to air, such as hydrogen.
- Toxic Gas Detection:
Electrochemical Detectors: Suitable for detecting toxic gases like hydrogen sulfide (H2S), chlorine (Cl2), ammonia (NH3), acrylonitrile, and carbon monoxide (CO).
Semiconductor Detectors: Also effective for detecting toxic gases and can be used in portable devices.
Photoionization Detectors (PID): These are useful for detecting volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as vinyl chloride.
Hydrogen Cyanide (HCN): Electrochemical detectors are the best option for HCN detection.
Benzene Detection: Both electrochemical and infrared detectors can be used effectively.
- Explosion-Proof Type and Level:
Explosion-Proof Certification: Ensure that the detectors comply with national standards such as GB50058, which outlines the requirements for electrical installations in areas with explosion and fire hazards.
- Sampling Method:
Diffusion Detectors: These are commonly used and require no additional sampling equipment. They are suitable for environments where the gas is expected to diffuse to the sensor.
Aspiration (Inhalation) Detectors: Used when diffusion detectors are not practical or when faster detection times are needed. These detectors actively draw in samples and can be more accurate in certain conditions.
By considering these criteria, you can select the most appropriate gas detector for your specific application, ensuring the safety and compliance of your industrial operations.
0